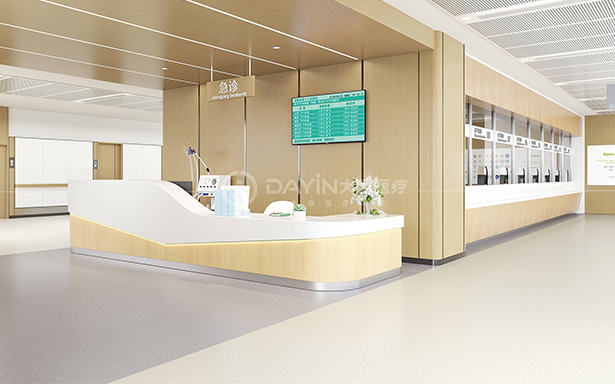
With the improvement of people's living standards, people's demand for the spiritual function of medical furniture is getting higher and higher, and in recent years, the design concept of "humanization" has become an irreversible design trend. As equipment that special groups of people in hospitals are in close contact with, humanization of medical furniture should be given an important height. Regarding humanized design, it should be understood from two aspects: one is from the perspective of psychology, that is, the respect and satisfaction of people's psychological and physiological needs and spiritual pursuits, the respect of human nature, and the humanistic care of design; the second is from the perspective of the relationship between people and furniture and other items and the space they constitute, that is, the perspective of ergonomics.
1. In line with the psychology of people in the hospital environment
Patients' psychology is hierarchical, namely psychological, physiological and social needs. Due to differences in gender, age, condition, background, etc., patients may have different psychological needs, expression intensity and environmental evaluation during the medical treatment process.
1. Patients’ psychological needs
Patients' psychology has three levels, namely psychological, physiological and social needs. Due to differences in gender, age, condition, background, etc., patients' psychological needs, expression intensity and environmental evaluation will differ during the medical treatment process.
Ordinary patients
Because these patients are not seriously ill and hope to return to their jobs as soon as possible after recovery, they are not very dependent on hospitals, but they have high requirements for the privacy and domain of the space. During the outpatient treatment process, ordinary patients have high requirements for human rights and attach importance to the experience of treatment. Because the outpatient clinic targets a wide variety of patients and various conditions have different symptoms, patients often show different psychological states. For example, when patients with acute trauma, excessive blood loss and shock come to see a doctor, they often show fear caused by unbearable pain, anxiety, tension, etc.; different diseases will also show different psychological states.


Elderly
As they age, their physical functions gradually decline. They suffer from illness for a long time and often need to go to medical institutions for physical examinations. The elderly are usually accompanied by their family members and relatives when they go to the hospital. But even with the company of their family members, the elderly are still very afraid of loneliness. They like to interact with others and have a nostalgic feeling. They like to chat about family matters or exchange medical treatment experiences while waiting for the doctor's visit. Therefore, when designing the public space of the hospital, it is necessary to design some quiet and sociable spaces for the elderly, and at the same time, special attention should be paid to the safety of the facilities.


child
Children do not have a comprehensive understanding of hospitals, so when they enter an unfamiliar medical environment, they are prone to panic, such as crying out of fear, fighting and being uncooperative. In addition, the pain and discomfort caused by the disease itself are also factors that easily cause children to panic in hospitals.


Gynecological patients
Gynecology and obstetrics are divided into gynecology and obstetrics. Most patients in gynecology clinics suffer from reproductive and other related diseases. Many patients feel very shy and difficult to talk about these diseases. Some unmarried women are under great psychological pressure and cannot communicate their conditions to doctors correctly, which greatly increases the difficulty of doctors' work. On the other hand, patients are prone to complex psychological reactions during registration and treatment. Any adverse stimulation can cause changes in patients' emotions and even sudden changes in their conditions.


2. Psychological needs of caregivers
Since family members do not come to see a doctor for the purpose of seeing a doctor, most of the time they accompany the patient to wait, rest, help the patient queue up for registration, get medicine, etc. They hope to know the patient's physical condition at the first time. Therefore, family members will focus more on the public space of the outpatient clinic, and hope that their behavior can be fairly implemented in the public space. Therefore, enough waiting furniture should be designed in the medical environment for caregivers to use. The furniture should be comfortable and warm to relieve the caregiver's fatigue and anxiety, and the arrangement of the furniture should have a sense of order. If necessary, the furniture can be equipped with guiding signs to maintain a fair waiting order.


3. Psychological needs of medical staff
The people who spend the longest time in medical spaces are medical staff. Most of them sit in for consultations or make rounds in wards and are in a stressful working state for a long time. Therefore, when designing the hospital environment, it is necessary to provide medical staff with sufficient space for communication, learning, rest, and a sense of security.


2. Ergonomics
Ergonomics emphasizes "people-oriented". Furniture products are for people to use. Therefore, the scale, shape, color and layout of furniture design must conform to the physiological and psychological scale of the human body and the activity rules of various parts of the human body to achieve the purpose of safety, practicality, convenience, comfort and beauty. For example, the edges and corners should be changed into rounded corners, and handrails should be designed to facilitate patients to stand up. At the same time, the color tone should be more lively and safe. Improper application of ergonomics in furniture design will increase the burden on patients, which violates the original intention of humanized design. The design should be designed according to the size of the person. For example, the side table design of the nurse station should be designed according to the average height of Chinese women; the design of the seat must also consider ergonomics. The seat height can be adjusted up and down, and the materials of the seat back and seat surface should have good breathability.


Medical furniture involves many parameters such as function, mechanics, and appearance. Compared with other furniture, medical furniture also has much higher requirements in terms of safety, humanization, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.




 400-9600-778
400-9600-778